Filter
667
Featured
Free Access
569
Quick Overview
5
Top Insights
20
Topics
Media Use, Media Consumption
202
Trust in the Media, Credibility of Media
122
Digital & Social Media Use, Internet Use
106
News Consumption & Information Sources of Media Users
61
Radio Consumption, Radio Use, Radio Audiences
58
Digital & Social Media Use: Youth
48
Television Consumption, Televison Use, Television Audiences
37
Access to Media & Information
35
Media Use: Youth
34
Disinformation, Misinformation, Fake News
34
Mobile Phone Use
29
Media Freedom, Press Freedom
27
Media Landscapes, Media Systems, Media Situation in General
25
Audience Feedback, Interaction & Participation
21
Community Radios
20
Digital & Social Media Use: Children
18
Television Use: Children
17
Online News
17
Access to Internet & Digital Communications
15
Media Use: Rural Populations
13
Media Use: Urban Populations
13
Information Needs
12
Print Media Use, Press Readers
12
Book Reading Habits, Book Readers, Book Consumption
11
Television Use: Youth
11
Watchdog Role of the Media
11
Information Needs & Media Use: Refugees & Displaced People
10
Media Use: Children
10
Media Use: Women, Female Media Audiences
10
Reading, Reading Habits, Reading Skills
10
Media Use: Catholic Media Productions
10
Conflict-Sensitive Radio Journalism, Radio in Conflict Prevention & Transformation
10
COVID-19 Communication
10
Children's Television Programmes
9
Edutainment Radio Programmes
9
Local Television
9
Digital Literacy: Youth
9
Media Literacy: Youth
9
Social Media
8
Local Radios, Local Radio Programmes
8
Public Media, State Media
8
Audience Segmentation, User Typologies, Personas
7
Community Radio Audiences & Use
7
Radio Use: Children
7
Media Use: Migrants & Diasporas
7
Radio Use: Youth
7
Media Viability & Financial Sustainability
7
Health Campaigns: Experiences
7
Access to Public Information, Freedom of Information, Right to Information
6
Film Audiences, Film Consumption
6
Gaming: Uses & Effects
6
Information Needs in Disasters & Humanitarian Crises
6
Milieus, Lifestyles
6
Rural Radio Programmes, Rural Radios, Rural Development & Radio
6
Digital Platforms & Intermediaries
6
Digital & Information Literacy
6
Financing Digital / Online Media
6
Facebook
6
Sexuality: Media Representation, Sexually Explicit Media Content, Pornography
6
HIV / AIDS Communication
6
Gender Advocacy & Empowerment, Gender Mainstreaming
5
Media Use: Entertainment
5
Media Use: Foreign / International Media
5
Media Use: Minorities & Disadvantaged Groups
5
Radio Use: Women
5
Religious Media Use, Religious Media Audiences
5
WhatsApp
5
Media Assistance
5
Refugees / Displaced People
5
Rural Communication, Media in Rural Areas
5
Digital Divide, Digital Inequalities
4
Agricultural Radio Programmes
4
Audience Expectations & Satisfaction
4
Disinformation Consumption & Perception
4
Health Information Access & Use
4
Media Use: Public Service & State Media
4
Mobile Phone Use: Women
4
Music Consumption & Use
4
Development Communication Campaigns
4
Catholic Radios
4
Perceptions & Attitudes Towards the Catholic Church
4
Cybersecurity, Digital Safety, Privacy, Right to Privacy
4
Digital Media Censorship, Control & Filtering, Internet & Social Media Censorship
4
Freedom of Expression
4
Community Participation in Community Media
4
Participatory Communication
4
Development Communication Projects: Case Studies
4
Behaviour Change Communication
4
Twitter & Microblogs
4
YouTube
4
Media Assistance: Disasters & Humanitarian Crises
4
Educational Radio Programmes
4
Open, Distance and Digital Education (ODDE)
4
Soap Operas & Telenovelas
4
International Radio Broadcasting, Foreign Radio Broadcasting
4
Local News
4
Television News
4
Media Assistance: Governance, Accountability, Combating Corruption
4
COVID-19 Pandemic: Effects on Journalism, Media & Communication
4
Financing Media: Customer Payments, Subscription Models, User-Based Financing
4
BBC
4
People with Disabilities: Access to & Use of ICT and Media
4
Civic Engagement, Citizen & Community Participation
4
Political Transition and Media
4
Public Service Broadcasting
4
Radio Dramas, Radio Soap Operas, Radio Fiction
4
Radio Programming, Programme Structures & Schedules
4
COVID-19 Pandemic: Economic, Political and Social Effects
4
Television
4
Agricultural Information & Extension
3
Audience Research
3
Media Use: Disasters & Humanitarian Crises
3
Mobile Phone Use: Youth
3
Book Markets & Industries
3
Catholic Television Programmes
3
Alternative Communication & Media
3
Community Television
3
Media Assistance in Conflict Regions & Fragile Countries
3
Media Assistance Projects & Programs: Case Studies
3
Development Journalism & Media Representation of Development Issues
3
Edutainment Health Programmes
3
Edutainment Television Programmes
3
Algorithms & Big Data
3
Cyberbullying, Cyberharassment
3
Democratization & Digital Media / Social Media
3
Instagram
3
Countering Hate Speech, Disinformation & Propaganda
3
Library Use
3
Media Markets
3
Television Entertainment, Television Entertainment Programmes
3
Women's Radio Programmes
3
Gender-Based Harassment, Intimidation & Violence
3
Health Radio Programmes
3
WASH Communication (Water, Sanitation, Hygiene)
3
Indigenous Radio Broadcasting
3
Satellite Television
3
Poverty & Impoverished People: Reporting & Media Representation
3
Religion: Media Representation
3
Media & Information Literacy
3
People with Disabilities: Tailored ICT & Media Products
3
Politics
3
Politics and Media
3
Democracy / Democratization and Media
3
Influence of Media on Politics
3
Political Television Programmes & Political Talkshows
3
Press
3
Radio Debates, Radio Talk Shows, Call-In Radio Programmes
3
Radio Stations
3
Media Effects
3
Preference
3
Television Reception & Effects
3
Research in Media & Communication
3
Mobile Phones, Smartphones
3
Cable Television
3
Youth, Adolescents
3
Youth Cultures, Youth Milieus, Youth Identities
3
Youth Television Programmes
3
Flow of Information
2
Advertising
2
Civic Engagement, Citizen Participation, Civil Society & Digital Communication
2
Civic Engagement, Citizen Participation, Civil Society & Media
2
Audiences & Users
2
Audience Research in Media Assistance
2
Elderly People: Internet & Social Media Use
2
Internet & Social Media Use: Women
2
Elderly People: Media Use
2
Media Socialisation, Media Biographies, Media Life Journeys
2
Media Use: Conflict Areas
2
Media Use: Indigenous Populations
2
Media Reception & Effects: Youth
2
Mobile Phone Use: Migrants & Refugees
2
Authoritarian Regimes: Media Systems & Landscapes
2
Catholic Book Publishing
2
Catholic Radio Programmes
2
Child Abuse: Digital Media
2
Child Protection Online
2
Christian Social Media Presence & Online Communities
2
Film Markets
2
National Cinemas, National Film Production
2
Public Diplomacy, Cultural Diplomacy
2
Community Radio Contents & Programming
2
Community Radio & Gender
2
Hate Speech, Hate Speech in Social Media
2
Television Quality
2
Rumours & Rumour Management
2
Perceptions & Attitudes Towards Development Issues and Development Assistance
2
Development Aid Reporting
2
Digital Media Landscapes
2
Internet
2
Podcasts
2
Sexual Abuse: Digital Media
2
Influencers (Social Media)
2
LinkedIn
2
TikTok
2
Streaming Media
2
Gender and ICTs / Internet
2
Radio in Disasters & Humanitarian Crises
2
Trust Building in Health & Emergency Communication
2
Election Campaigns: Disinformation & Misinformation
2
Libraries
2
Radio Markets
2
Video on Demand
2
Labour, Labour Markets, Labour Laws, Working Conditions
2
Climate Change Communication, Climate Journalism
2
Gender and Radio
2
Gender Relations
2
Gender Representation & Stereotypes in the Media
2
Media Assistance: Gender Focus
2
Media Reception & Effects: Women
2
Food / Nutrition Communication & Media Representation
2
Sexual Health Communication, Reproductive Health Education, Family Planning
2
Indigenous Media, Indigenous Language Media Productions
2
China: Transnational Information Operations, International Broadcasting, Public Diplomacy
2
Foreign Television Programmes
2
Image Abroad
2
Transnational Television, International Television
2
Journalistic Quality
2
Radio News
2
Election Reporting
2
Local Communication & Media
2
Media Assistance: Radio
2
Media Assistance: Television
2
Communication & Information Needs
2
Diversity & Pluralism in Media / Communication
2
Interpersonal Communication, Interpersonal Relations
2
Media, Mass Media
2
Child Protection: Legislation & Regulation
2
Migration & Refugees Reporting & (Social) Media Representation
2
Peace, Peacekeeping, Peace Building, Peace Movements
2
Election Campaigns: Social Media
2
Governance & Accountability: Role of Media / Communication
2
Governance & Accountability as Focus of Radio Programmes
2
Opinion Leaders, Politicians, Decision Makers, Elites
2
Newspapers
2
Public & State Radios
2
Radio
2
Business & Economics Radio Programmes
2
Youth Radio Programmes, Youth Radio Stations, School Radios
2
Habits
2
Everyday Life
2
Perception, Cognition & Comprehension
2
Uses-And-Gratifications Approach
2
Population
2
SMS
2
RT (Russian International Broadcaster, formerly Russia Today)
2
Television Programmes & Genres
2
Suburbs, Poor Districts, Slums, Shanty Towns
2
Youth and Media
2
Youth Activism, Youth Civic Engagement, Youth Political Interests, Youth Protests
2
Youth & Digital Media
2
Access to Media & Information: Disadvantaged Groups and Minorities
1
Adblocking
1
Advertising Markets & Industries
1
Advocacy & Empowerment: Disadvantaged & Vulnerable Groups
1
Advocacy & Empowerment: Youth
1
Digital Activism, Cyber Advocacy
1
People with Disabilities: Advocacy & Empowerment
1
Shamba Shape Up (Agricultural Reality TV Programme, Kenya)
1
Audience Composition
1
Audience Research Methods
1
Community Media Audiences & Use
1
Internet & Social Media Use: Minorities
1
Information Use & Consumption
1
Interactive Radio: Audience Participation, Interaction & Feedback
1
Mobile Phone Use: Children
1
Reading Habits: Children
1
Media Use: Families
1
Media Use: Foreign & International News
1
Media Use: Influence of Religion
1
Media Use: Lower Classes & Poor Population
1
Mobile Phone Use: Minorities
1
Media Use: Political Information
1
Media Use: Preferred Contents & Programmes
1
Television Use: Women
1
Independent & Oppositional Media in Authoritarian Regimes
1
Books
1
Bestsellers
1
Book Trade & Distribution
1
Bookshops & Bookshop Management
1
Children's Books & Literature
1
E-Books & Digital Book Publishing
1
Campaigning
1
Campaigning: Effects & Effctiveness
1
Election Campaigns
1
Radio Campaigns
1
Catholic Church and Communication
1
Catholic Digital Media Presence & Online Communities
1
Catholic Libraries
1
Catholic Press
1
Radio Maria (Catholic Radio Network)
1
Catholic Television
1
Madha TV (Catholic Television Channel, Tamil Nadu)
1
Rede Vida (Catholic Television Channel, Brazil)
1
Catholic Websites
1
Diocesan Catholic Communication Work
1
Catholic Religious Congregations, Catholic Orders
1
Children and Media
1
Animated Cartoons, Animated Films
1
Child Protection, Protection of Minors
1
Digital Media Socialisation
1
Children: Early Childhood, Toddlers, Preschoolers
1
Children's Media
1
Girls and Media
1
Media Literacy: Children
1
Media Reception & Effects: Children
1
Televangelism
1
Urban Pastoral
1
Digital Theologies
1
Environmental Films
1
Educational Films & Videos
1
Indigenous Films, Indigenous Videos
1
Bollywood
1
Film Language
1
History of Film & Cinema
1
Communication Rights
1
Exile Journalism, Exile Media
1
Freedom of Expression Online, Internet Freedom
1
Censorship
1
Indirect Censorship, Soft Censorship
1
State Influence on the Media
1
Community Communication
1
Community Media
1
Community Media Policies & Regulation
1
Community Radio Management
1
Community Radio Sustainability & Financing
1
Groups, Group Communication, Group Development
1
Media Assistance: Community Radios
1
Traditional Communication
1
Conflicts, Conflict Prevention & Management, Mediation, Peacebuilding
1
Russia-Ukraine War <2014-
1
Conflict Areas: Media Systems, Media Landscapes, Role of Media
1
Conflict Reporting, Armed Conflict Reporting
1
Conflict-Sensitive / Peace Communication
1
Conflict-Sensitive & Peace Journalism
1
Extremist & Terrorist Digital / Social Media Presence
1
Extremist & Terrorist Communication Strategies and Media
1
Foreign Conflict Reporting, International War Reporting
1
Media Assistance: Conflict Prevention, Mediation & Reconciliation
1
Transitional Justice Reporting
1
Violence in the Media: Reception & Effects
1
War Reporting
1
Contents of Media
1
Radio Quality
1
Theatre
1
Cultural Policies
1
Cultural Development
1
Gaming: Youth
1
Literature
1
Religion and Culture
1
United States Agency for International Development (USAID)
1
Development Communication, Communication for Development (C4D)
1
Development Communication: Effects & Effectiveness
1
Soul City (NGO, South Africa)
1
Development Education: Use & Role of Media
1
Entertainment Education, Edutainment
1
Edutainment Campaigns: Experiences
1
Edutainment: Youth
1
Radio for Development
1
Rural Communication for Development
1
Big Digital Platforms, Big Tech Companies
1
Digital Ethics, AI Ethics, Social Media Ethics, Data & Information Ethics
1
Religious Apps
1
Digital Platform & Intermediaries Regulation
1
E-Governance, E-Democracy
1
Google
1
Interactive Media
1
Internet and Politics
1
Internet / ICTs and Social Change
1
Media Assistance: Digital Journalism & Social Media
1
Digital Financial Services, Mobile Banking, Mobile Payphone Business
1
Digital Journalism, Online Journalism
1
Digital Political Communication
1
Political Websites & Online Communities
1
Digital Media Markets
1
Online Radio, Internet Radio, Radio Streaming
1
Netflix
1
Sexting (Sending Sexually Explicit Messages of Oneself to Others)
1
Social / Digital Media and ICTs in Disaster & Humanitarian Crisis Management & Prevention
1
Social Media & Web 2.0 for Development
1
Digitalization, Digital Transformation
1
Educational Use of ICTs / Internet
1
Online Learning, E-Learning
1
Mobile Phone Markets
1
ICT Policies
1
Albinism
1
Ethnic Media, Minority Media
1
Ethnic / Minority Radio Programmes
1
Integration of Minorities: Role of Media
1
Minorities & Disadvantaged Groups: Reporting & Media Representation
1
Perceptions & Attitudes Towards Minorities
1
Religious Minorities & Media
1
Disaster & Humanitarian Crisis Communication
1
Disaster & Humanitarian Crisis Information Management
1
Disaster Risk & Preparedness Communication, Disaster Prevention Communication
1
Conspiracy Narratives, Conspiracy Theories
1
Health Disinformation & Misinformation
1
Identifying & Researching Disinformation
1
Library Marketing & Library Image
1
Public Libraries
1
Television Industries
1
Local Media Economics & Markets, Local Media Financing
1
Media Ownership
1
Poverty & Poverty Reduction
1
Energy Supply, Electricity
1
Education and Communication / Media
1
Adult Education
1
Easy-To-Understand Information, Easy-To-Read Materials, Easy Language
1
Radio Schools
1
Educational Television
1
Educational Communication
1
Schools
1
Educational Games, Serious Games
1
Students
1
Gaming, Video Games
1
Addiction to Media & Video Games, Effects of Media on Mental Health
1
Television Entertainment: Audiences
1
Communication for Sustainable Development
1
Environmental Journalism
1
Fact-Checking & Verification of Sources
1
Sensationalist Journalism, Yellow Press
1
Female Journalists & Media Workers
1
Women's Television Programmes
1
Gender-Based Online Harassment & Sexual Threats
1
Gender Discrimination, Gender Inequalities
1
Marriage & Partnership
1
Rural Women & Communication
1
Women with Disabilities & Media
1
Health Communication
1
Food, Food Security, Nutrition
1
Health Communication & Campaigns: Youth
1
Health Journalism
1
Malaria Communication
1
Vaccination Campaigns & Vaccine Hesitancy
1
Indigenous Languages
1
Intercultural Communication, Intercultural Competencies
1
Developing Countries Reporting & Representation in Foreign / International Media
1
Foreign News, International News
1
Russia: Foreign Information Operations, International Broadcasting, Public Diplomacy
1
Russia: Foreign Media Representation & Image Abroad
1
Sputnik (Russian State News Portal & Radio Broadcast Service)
1
Journalism
1
Constructive Journalism, Solution-Oriented Journalism
1
Crossmedia Journalism
1
Media Assistance: Journalism Education & Training
1
Local Journalism
1
News
1
News Reception
1
Radio Journalism
1
Radio Interviews
1
Business & Economics Journalism
1
Protests, Protest Movements, Protest Reporting & Media Representation
1
Religious Journalism, Religion News
1
Service Journalism, Consumer Information, Lifestyle Journalism
1
Working Conditions of Journalists & Media Personnel
1
Bilingualism, Multilingualism
1
Media Assistance: Elections
1
Media Assistance: Financial Sustainability & Management
1
Fondation Hirondelle
1
Media Assistance: Institutional Support & Core Funding
1
Media Assistance: Youth Programmes & Media
1
Information
1
Information Ecosystems
1
Stereotypes in Media & Communication
1
Trust Building: Role of Communication & Media
1
Radio Policies
1
Media Law & Regulation
1
Licensing of Media
1
Marketing & Branding
1
Quality Criteria, Quality Standards
1
Religious Media Management & Financing
1
Radio Sawa
1
Radio Television Afghanistan (RTA)
1
Migrants & Refugees: Tailor-Made Media Products & Information Services
1
Radio Music
1
Governance
1
Government
1
Political Opposition
1
Political Participation
1
Political Parties
1
Democratization
1
Fragile / Post-Conflict States
1
National Identity & Media, Nationalism & Communication
1
Radicalisation: Influence of Media
1
Public Service Broadcasting: Religious Programmes
1
Radio Programmes & Genres
1
Radio Reception, Radio Psychology, Radio Effects
1
Commercial Radios
1
Mega FM (Radio Station, Gulu, Uganda)
1
Radio Chiwalaki (Vacas, Cochabamba, Bolivia)
1
Radio Madang (Papua New Guinea)
1
Radio Progress (Wa, Upper West Region, Ghana)
1
Audience Influence
1
Digital Wellbeing, Digital Resilience, Digital Mental Health
1
Emotions in the Media, Emotional Functions & Messages of Media
1
Media Psychology, Communication Psychology
1
Media Reception
1
Media Reception & Effects: Rural Population
1
Social Participation
1
Mental Stress
1
Personality
1
Social Functions & Effects of the Media
1
Interreligious Dialogue
1
Islamist Communications & Media
1
Muslim Digital Media & Online Communities
1
Muslim Television Broadcasting
1
Perceptions & Attitudes Towards Religion
1
Youth & Religion
1
Data Collection, Data Collection Methods
1
Internet & ICTs in Rural Areas
1
Mobile Phones in Rural Areas
1
Rural Television
1
Science Communication & Research Dissemination
1
Social Conflicts, Social Problems
1
Society
1
Rohingya
1
Participation
1
Reality & Communication, Truth & Media
1
Social Aspects
1
Social Change
1
Theories of Change
1
Social Classes
1
Lower Classes
1
Sociology
1
Stigmatization
1
Digital Television
1
Short Wave Radio (SW)
1
Satellite Communication & Information Services
1
WLAN Wireless Internet Access
1
Pay TV, Pay Television
1
Television Channels
1
Al-Arabiya
1
Al-Hurra (Television Channel)
1
Al-Jazeera
1
Reality Television Programmes & Daily Talks
1
Television Talk Shows
1
Television Programming, Programme Structures & Programme Policies
1
Theories of Communication & Media
1
Urban Communication, Urban Media
1
Language
Document type
Countries / Regions
Authors & Publishers
Media focus
Publication Years
Methods applied
Journals
Output Type
Understanding How Young Cambodians (15-30 Year Olds) Use Media and Information: Key Findings
BBC Media Action (2021), 6 pp.
"Social media is the most popular form of media, consumed by 87% of 15-30 year old Cambodians. Nevertheless, traditional mass media (television and radio) remain important, particularly for more vulnerable groups. For example, TV usage is higher amongst women, those from rural locations, and those f
...
Ethiopians Support Media’s Watchdog Role But Want Regulated Access to Internet, Social Media
Afrobarometer (2021), 13 pp.
"Six in 10 adult Ethiopians (59%) own a mobile phone. But only 16% own a phone with Internet access. One in three (34%) own a radio, while 14% have a television set and only 2 % have a computer. The most common source of regular news (“every day” or “a few times a week”) for Ethiopians is th
...
"To gain a comprehensive understanding of both urban and peri/urban/rural locations, the assessment was conducted in two locations in Ethiopia: Gambella Region and Addis Ababa City Administration. A total of 240 respondents participated in the assessment, of which about one-third are female. The fin
...
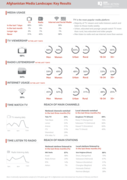
Afghanistan Media Landscape: Key Results
London: BBC Media Action (2021), 1 p.
"TV is the most popular media platform. Majority of TV viewers and radio listeners watch and listen to those media weekly. Urban, educated and younger people watch TV more than rural, less educated and older people. Men listen to radio and use internet more than women [...] A nationally representati
...
La radio: El medio de comunicación que llega al 80 % de personas diariamente
Lima: CPI (2021), 6 pp.
"La pandemia del Covid 19 generó notables cambios en los hábitos de consumo de las personas y su interacción con los medios. Como consecuencia del aislamiento social, las personas buscaron fuentes de información y entretenimiento confiables y de fácil acceso, por lo que la radio incrementó su
...
"Through a combination of interviews, surveys, desk research, and focus group discussions this Information Ecosystem Assessment (IEA) explores trends of information demand and supply within refugee and host communities. The report analyzes their information access, needs, use, flows, and identifies
...
Peruano digital
Lima: Ipsos Perú (2021), 1 p.
"Se estima que 9.1 millones de peruanos son digitales. Representan el 54% de la población urbana de 18 a 70 años." (Página 1)
Marginalized Religious Communities in Indonesian Media: A Baseline Study
Remotivi; International Media Support (IMS) (2021), 68 pp.
"This study finds that the Indonesian media ecosystem is not a safe space for marginalized religions. As explained in the conclusion to the content analysis, the space given by the media for news coverage of marginalized religious groups is still very small. Although non-Islamic official religions e
...
Media and Information Landscape in Lebanon
Internews; Maharat Foundation (2021), 59 pp.
"Through a combination of qualitative in-depth interviews with alternative media outlets, quantitative audience surveys involving over 1500 respondents, and focus-group discussions with women and youth civil society actors, this media and information landscape (MILA) evaluates the level of trust tow
...
Hygiene and Behaviour Change Coalition Project: Reach and Engagement Survey Afghanistan
London: BBC Media Action (2021), 4 pp.
"BBC Media Action is helping to reduce the transmission of the coronavirus in Afghanistan by using a media campaign to encourage uptake of preventive behaviours. Informed by research the project’s media outputs aim to help reduce the transmission of the coronavirus by encouraging take up of the fo
...
"En Barranquilla y Soledad se destacan tres categorías de necesidades de información entre la población migrante y retornada: información legal/asuntos migratorios (76%); medios de subsistencia (63%, incluye información laboral); necesidades primarias (55%, esta categoría incluye los temas de
...
The Kenya Media Assessment 2021
Internews (2021), 47 pp.
"There are stark lessons to be learnt from this assessment: Social media has become the main source of news and information for majority of Kenyans, even though it suffers the greatest trust deficit. Radio remains highly important, while television is the most trusted source of information and newsp
...
Mainzer Langzeitstudie Medienvertrauen 2020: Medienvertrauen in Krisenzeiten
Media Perspektiven, issue 3 (2021), pp. 152-162
"In der siebten Befragungswelle der Mainzer Langzeitstudie wurde ein deutlich gestiegenes Vertrauen in die Medien festgestellt. Den Medien scheint es 2020 gelungen zu sein, als Orientierungspunkt zu dienen und die Menschen mit Informationen zu versorgen. Auch der in den Vorjahren zu beobachtende Med
...
State of the Media Survey Report 2021
Nairobi: Media Council of Kenya (2021), xii, 46 pp.
"The survey found that 58% of Kenyans interviewed consume TV content on a typical day. This translates to approximately 16,740,493 Kenyans aged above 15 years who consume TV content. This is a drop from 74% of the respondents recorded in the 2020 survey. Across the regions, 60% of persons in North E
...
Georgia: An Information Ecosystem Assessment
Internews (2021), 3 parts
"Internews’ Global Tech and Europe & Eurasia teams conducted an extensive information ecosystem assessment (IEA) study in Georgia with a team of local researchers and experts. This IEA examines every region in Georgia, including minority language communities, and adopts a specific focus on social
...
Edelman Trust Barometer 2021: Global Report
Edelman (2021), 58 slides
"After a year of unprecedented disaster and turbulence – the Covid-19 pandemic and economic crisis, the global outcry over systemic racism and political instability – the 2021 Edelman Trust Barometer reveals an epidemic of misinformation and widespread mistrust of societal institutions and leade
...
Online Survey on Youth, Social Media, and Violence in Sri Lanka
London: British Council (2021), 103 pp.
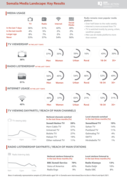
Somalia Media Landscape: Key Results
London: BBC Media Action (2021), 1 p.
"Radio remains most popular media platform. Over half listen to the radio weekly. Internet is more accessed than TV. TV is watched mostly by young, urban, wealthier people. Men use all media platforms more than women [...] A nationally representative sample of 2,004 adults aged 18+ in Somalia were i
...